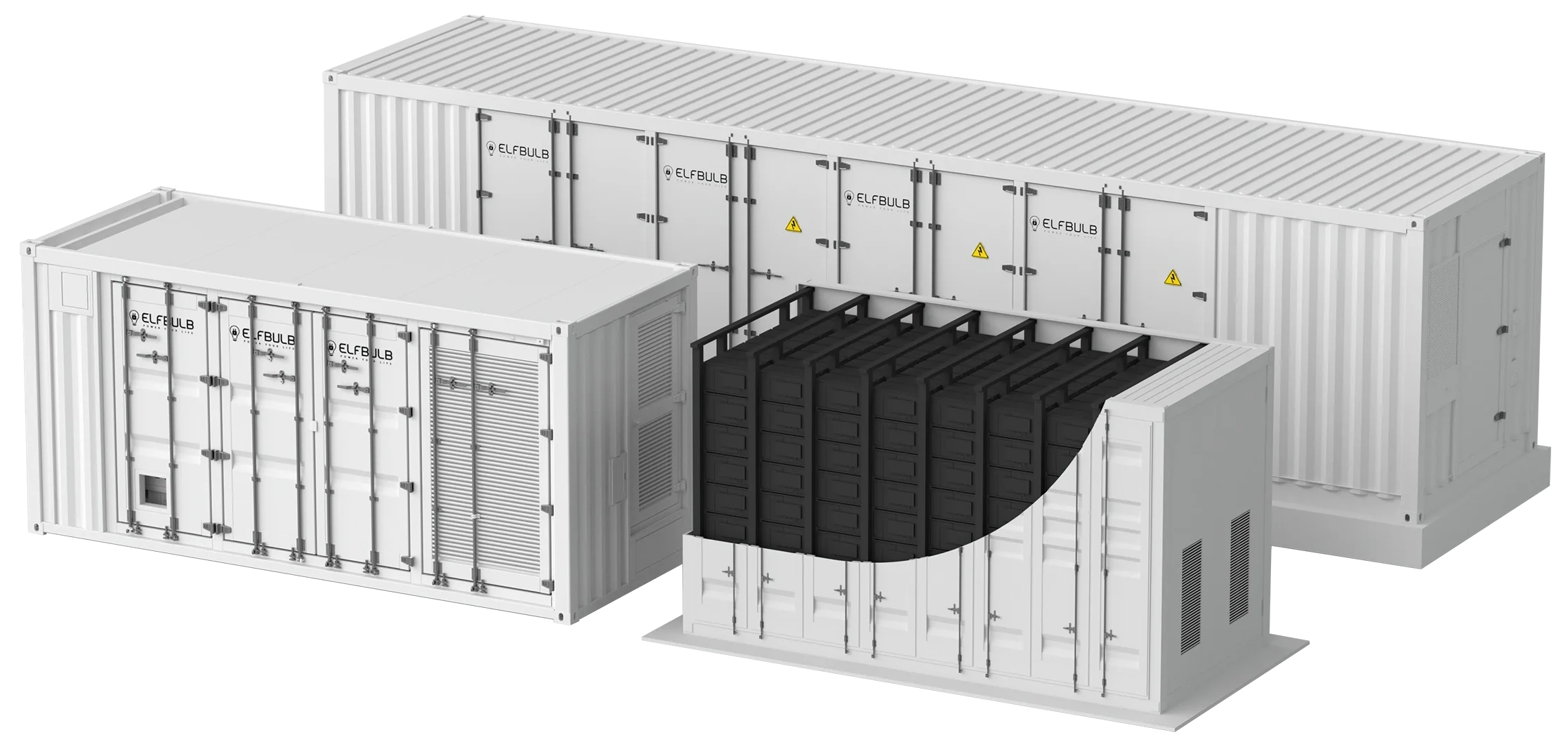
Off-Grid PV-BESS (With Diesel/Wind Option)
Case description
Islanded Grid: A closed power supply network operating independently of the main grid, which needs to maintain frequency and voltage stability autonomously.
Load-side Energy Storage: An energy storage system installed at the user’s power consumption end (such as factories, communities), directly serving local load demands.


Power Supply Guarantee for Remote Islands/Areas without Grid Coverage Scenario
• Characteristics: suitable for islands, many remote islands lack main grid coverage, relying on diesel generators for power supply (high cost, heavy pollution).
• Role of Energy Storage:Combined with renewable energy sources such as photovoltaic (PV) and wind power, it forms a "PV-storage-diesel" or "wind-storage-diesel" hybrid system to reduce diesel consumption (e.g., small islands around Bali).
• When renewable energy output is insufficient, the energy storage system quickly discharges to supplement energy and avoid power outages (e.g., when PV stops generating at night).
Off-grid Power Supply for Industrial Parks/Mining Areas
• Scenario Characteristics: Resource development areas such as nickel and coal mines in Indonesia are mostly located in remote regions, requiring self-built independent grids to meet high-load production needs (e.g., electrolytic nickel plants).
• Value of Energy Storage:Smoothing load fluctuations: When industrial equipment starts or stops, the energy storage system rapidly adjusts power to prevent grid voltage dips (e.g., when a mine crusher starts).
• Reducing power costs: Using energy storage to charge during low electricity price periods and discharge during peak periods to optimize enterprise power costs (if a microgrid tariff mechanism is configured within the islanded grid).
"Backup Power + Frequency Regulation" in Areas with Unstable Main Grid
• Scenario Characteristics: Although some islands in Indonesia are connected to the main grid, power outages or voltage fluctuations often occur due to weak grids (e.g., eastern Java Island).
• Functions of Energy Storage:Switching to off-grid mode in milliseconds to serve as backup power for critical loads such as hospitals and communication base stations (similar to UPS function).
• Participating in grid frequency regulation through rapid charging and discharging (e.g., when the main grid frequency fluctuates, the energy storage system automatically charges/discharges to stabilize the frequency).
Integration and Consumption of Renewable Energy
• When PV/wind power generation is high, the energy storage system charges to store excess electricity and avoid curtailment (e.g., PV power plants in Sumatra equipped with energy storage).
• When renewable energy output decreases, energy storage discharges to maintain power supply continuity and improve energy utilization efficiency.
Off-Grid Energy Storage Solution
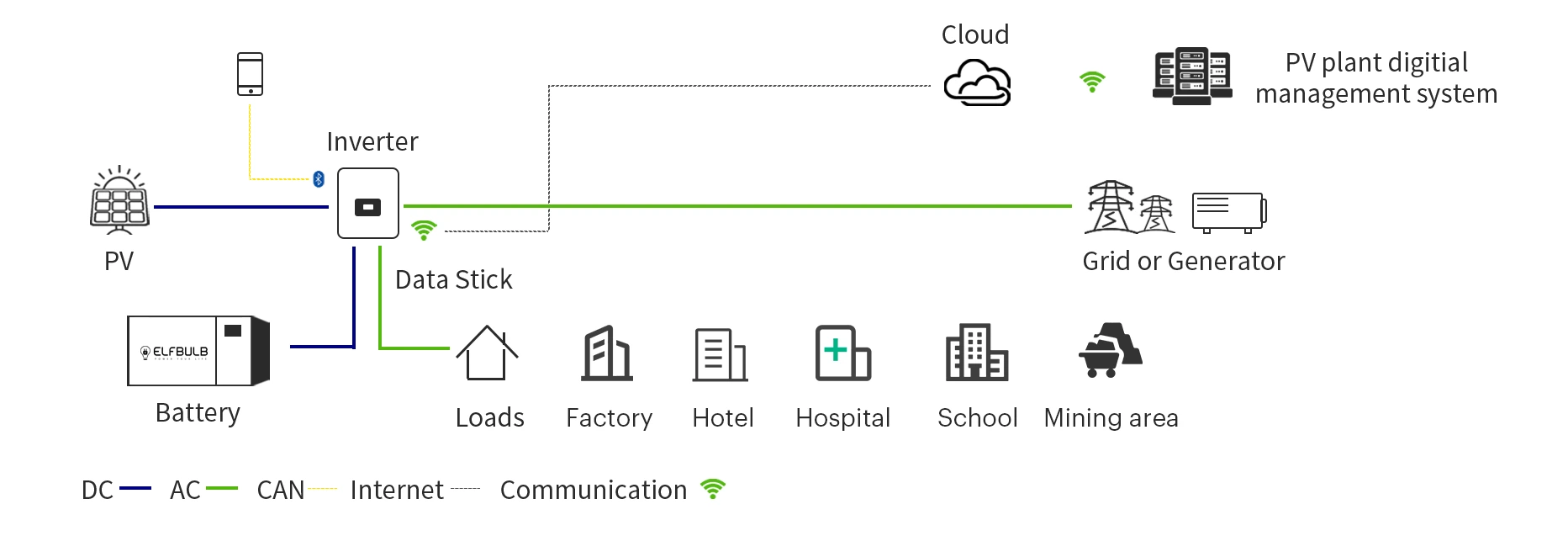
Application Scenarios







