1. What is BMS?
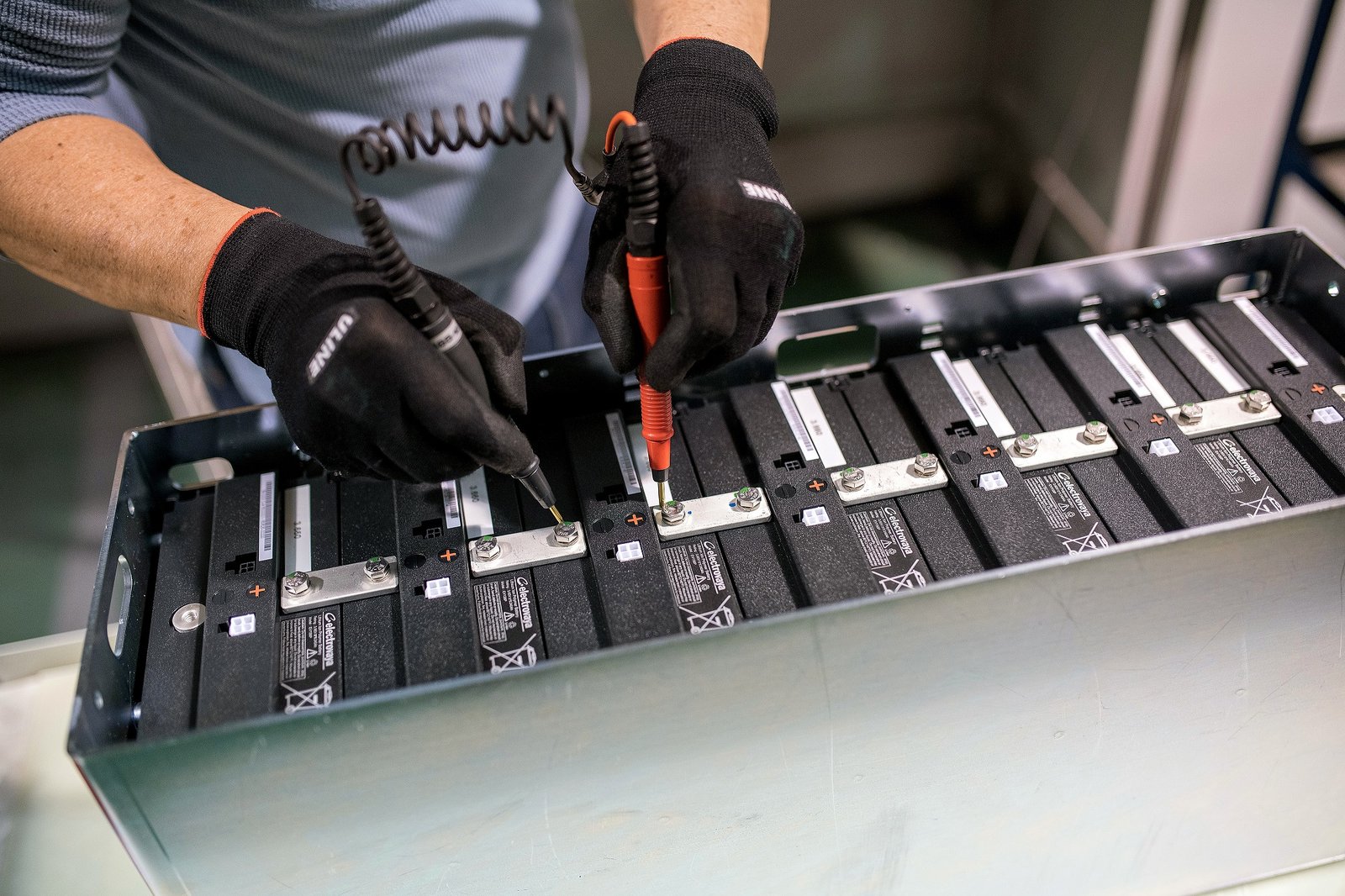
A Battery Management System (BMS) is an electronic system designed to manage rechargeable batteries (individual cells or battery packs). It monitors and estimates various battery states, calculates secondary data, reports this information, and controls the battery environment to ensure safe usage and extend battery life.

2. Key Functions of BMS
2.1 Monitoring Battery State
- Voltage: Monitors total voltage, voltage of individual battery cells, or voltage at periodic sampling points.
- Temperature: Records average temperature, coolant inlet temperature, coolant outlet temperature, or temperature of individual battery cells.
- Current: Tracks battery charging and discharging currents.
2.2 Battery Charging Control
- BMS controls the battery charging process, including re-injecting recovered energy (e.g., regenerative braking energy) back into the battery pack.
2.3 Battery Thermal Management
- Passive or active methods are used for battery thermal management, with coolants ranging from air to liquids or phase-change materials.
- Air cooling is simple but less efficient, while liquid cooling offers higher heat dissipation potential but requires more complex systems.
2.4 Calculation of Secondary Data
- Minimum and maximum voltage of battery cells.
- State of Charge (SoC) or Depth of Discharge (DoD) to indicate battery charge level.
3. Importance of BMS
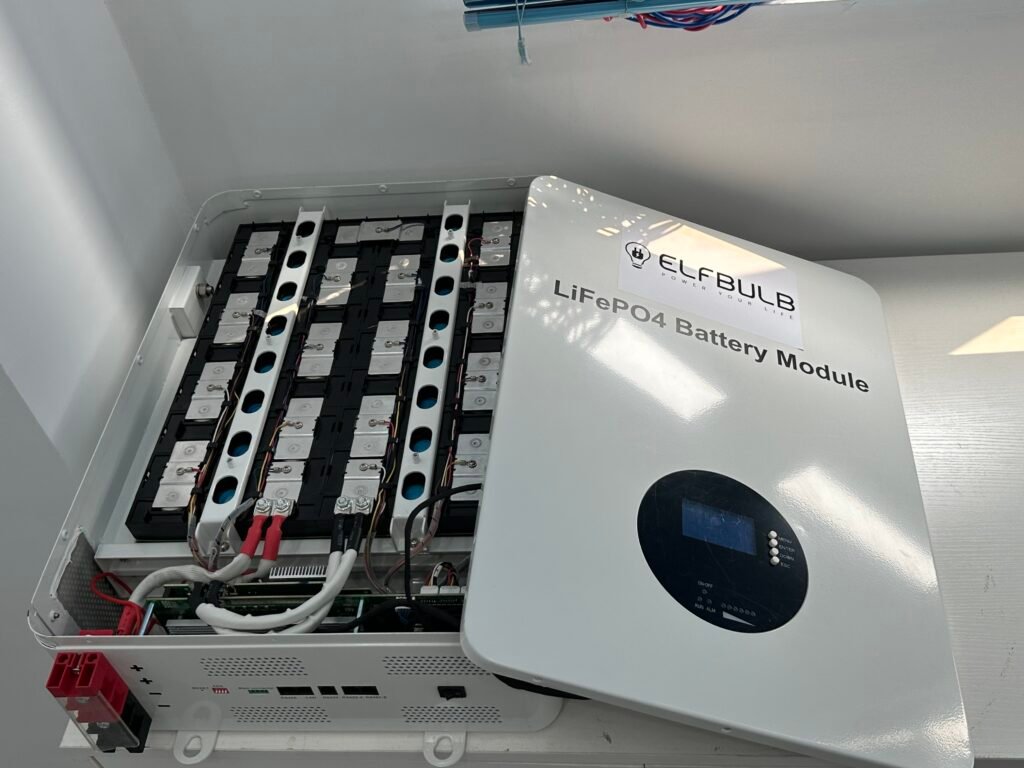
BMS is a critical component for ensuring safe battery operation and extending lifespan. It is widely used not only in electric vehicles but also in solar energy storage systems, drones, portable devices, and more.
Whether for environmental or economic reasons, optimizing battery performance and safety remains crucial. Ongoing BMS development and innovation will continue to drive advancements in battery technology.